In today’s automotive world, the demand for high-performance, durable, and highly precise components is greater than ever. Behind every reliable engine, suspension system, or transmission assembly is a complex network of precision parts — many of which owe their existence to advanced automotive machining processes.
Automotive machining is a cornerstone of manufacturing this new generation of auto parts. From concept design to mass production, machining ensures that every component meets stringent requirements for accuracy, strength, and longevity. At the forefront of this industry are firms like Chiheng Hardware, which specialize in CNC machined automotive components serving OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), aftermarket suppliers, repair shops, and performance companies worldwide.
Table of Contents
What Is Automotive Machining?
Automotive machining refers to the set of precision processes used to manufacture parts for vehicles, both standard and custom. These processes use cutting tools, rotary spindles, and high-precision machines to remove material from a workpiece to create a finished automotive component. Production tolerances are often extremely tight, reflecting the critical nature of the parts.
At its core, automotive machining includes operations such as:
- Turning — rotating the workpiece while cutting tools shape it.
- Milling — cutting features like planes, slots, or complex profiles.
- Drilling and Tapping — creating precise holes for fasteners or fluid passages.
- Grinding and Honing — fine finishing for surface quality and dimensional precision.
- Threading — producing screw threads for fasteners or assemblies.
- Surface Finishing — additional treatments for durability and performance.
Machining processes may vary depending on the part’s design, material, and required specifications. But one thing remains consistent: precision and reliability dominate the decision-making process.
The Role of CNC in Automotive Machining
Central to modern automotive machining is CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology. CNC machined automotive components are produced by automated machines that follow pre-programmed instructions — often derived from 2D drawings or 3D CAD models — to deliver consistent, repeatable precision across parts.
CNC machines can operate in multiple axes — such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis configurations — allowing them to perform complex cuts and shapes with minimal human intervention. This not only improves accuracy but also supports quicker turnaround times and lower error rates.
Because today’s vehicles demand parts that function under high stress and performance loads, CNC machining ensures components fit exactly, work correctly, and withstand mechanical stress in real-world conditions. This is why CNC machined automotive components are widely used in critical applications like engine parts, transmissions, braking systems, suspension mounts, and more.
Materials Used in Automotive Machining
One of the defining aspects of automotive machining is the variety of materials that engineers work with. Depending on the component’s application, performance requirements, and environmental exposure, different metals and plastics are used.
Here are common materials used in automotive machining:
Metals
- Aluminum (e.g., 6061, 7075): Lightweight with excellent strength-to-weight ratio — ideal for engine brackets, housings, and structural components.
- Steel Alloys (e.g., Mild Steel 1018/1045): High strength and durability make these ideal for shafts, gears, and load-bearing parts.
- Stainless Steel (e.g., 304/316): Excellent corrosion resistance — perfect for exhaust components and exposed hardware.
- Titanium: Combines high strength with lightweight properties, often found in high-performance tuning or racing applications.
- Brass and Copper: Used in fittings, connectors, and precision components requiring excellent machinability.
Plastics
Modern automotive components increasingly incorporate advanced plastics and engineering polymers. These materials are used for lightweight housings, gears, clips, interior components, and more:
- Nylon (PA): Durable and low friction.
- ABS and PC: Common in interior trim and non-structural parts.
- PEEK and POM (Delrin): High-performance polymers for demanding environments.
This wide range of materials allows automotive machining to support components across the entire vehicle — from engine internals to aesthetic exterior parts.
Precision and Tolerance: What It Means for Auto Parts
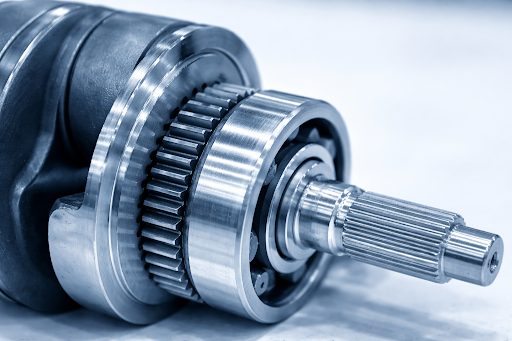
When discussing automotive machining, precision and tolerance are two of the most critical concepts.
Tolerance refers to how much deviation is acceptable between the design dimensions and the actual machined part. In automotive manufacturing, tolerances must be incredibly tight — often as low as ±0.005 mm — to ensure parts fit together properly and perform safely.
Achieving such precision requires:
- High-quality CNC equipment (3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis machines).
- Skilled machinists and engineers who program, monitor, and verify operations.
- Rigorous quality control with measuring tools and dimensional inspection.
Precise machining is vital for functional assemblies such as:
- Engine components: Pistons, crankshafts, camshafts — all of which must operate within microns of tolerance.
- Transmission gears: Precision geometry ensures smooth shifts and durability.
- Brake parts: Tight tolerances directly contribute to safety and performance.
- Steering and suspension components: Accurate machining prevents premature wear and improves vehicle stability.
The Importance of CNC Machined Automotive Components
Automakers, aftermarket fabricators, and performance tuners rely on CNC machined automotive components because of the proven business and production advantages CNC technology delivers. Understanding the broader benefits of using CNC machines helps manufacturers appreciate why CNC machining remains essential for scalability, cost control, and consistent product quality.
1. Consistent Accuracy
CNC processes follow digital instructions that ensure each part is produced exactly as specified — a critical requirement for safety and performance in automotive applications.
2. Scalability From Prototype to Production
Whether producing a single prototype test piece or scaling to large-volume production, CNC machining supports both without sacrificing quality.
3. Complex Geometry Capability
Many automotive parts have intricate shapes, curves, pockets, and features that would be difficult or impossible to produce with manual methods — CNC machines handle these with precision.
4. Material Flexibility
From tough steels to high-performance plastics, CNC machining accommodates a wide range of automotive materials — giving engineers freedom to choose the right material for each job.
How Automotive Machining Works at Chiheng Hardware
Companies like Chiheng Hardware specialize in automotive machining services that combine cutting-edge technology, global manufacturing experience, and quality management systems.
Here’s how their process typically works:
1. Design Review and Quotation
Customers submit CAD files or technical drawings. Engineers review specifications — including material, tolerance, and surface finish — and provide a detailed quote.
2. Material Preparation
Based on the design requirements, appropriate metals or plastics are selected. Each raw material is inspected to ensure it meets quality standards.
3. CNC Programming
Experienced CAM programmers convert digital designs into machine code that governs tool paths and machining sequences.
4. Machining Operations
Using advanced CNC mills and lathes, components are machined to exact dimensions. Multiple operations may be performed — including turning, milling, drilling, threading, and more — depending on the part.
5. Quality Inspection
Before delivery, every component undergoes dimensional inspection to ensure it meets tolerance requirements. Any deviations are corrected before approval.
6. Surface Finishing
Parts may be polished, plated, heat-treated, or coated according to customer specifications — improving performance and longevity.
7. Delivery
Finished components are shipped globally — whether as standalone parts, large-batch runs, or prototype sets.
This systematic approach ensures CNC machined automotive components are not only accurate and dependable but also ready for real-world use — in OEM production, repair facilities, or custom automotive projects.
Typical Automotive Components Produced by CNC Machining
CNC machining supports a broad range of automotive parts, including but not limited to:
- Engine Mounts and Housings
- Gears and Splines
- Brake Components
- Transmission Shafts
- Suspension Brackets
- Bearing Housings
- Custom Performance Parts
Precisely machined parts help vehicles achieve greater efficiency, enhanced safety, and longer service life — especially in demanding environments such as high-performance or off-road vehicles.
Why Precision Matters in the Automotive Sector
Vehicles operate under high mechanical loads, extreme temperatures, and demanding environmental conditions. This is why mistakes or variations — even in microns — can cause malfunction, reduced performance, or safety hazards.
Precision machining ensures:
- Proper Fit: Parts align perfectly within assemblies.
- Smooth Performance: Reduced friction and vibration.
- Reliability: Consistency across every unit produced.
- Longevity: Less wear and tear over time.
Conclusion
Automotive machining is a foundational element of the modern vehicle manufacturing ecosystem. From the smallest precision component to major structural parts, CNC machined automotive components ensure vehicles operate safely, reliably, and efficiently.
With advanced manufacturing capabilities — including multi-axis CNC machining, tight tolerance control, and comprehensive material expertise — companies like Chiheng Hardware are shaping the future of automotive part manufacturing. Whether you’re producing prototype parts or supplying components for global markets, precision machining delivers the performance, quality, and confidence that today’s automotive industry demands.